What is an Engineering Checklist?
An engineering checklist is a form used by engineers to ensure that standard protocols, safety measures, client specifications, and other important directives are understood, confirmed, and adhered to during the progression of engineering projects. It serves as a valuable tool to help prevent errors, identify potential issues, and ensure that all necessary steps are taken. These checklists can be customized depending on the field or project they’re used for, including design, construction, testing, maintenance, or any other engineering activity.
What are Engineering Projects?
Engineering projects are a set of activities planned by a cross-functional team of engineers to execute commissioned work and fulfill client requirements. These projects generally involve the design, manufacturing, and distribution of products or the design, construction, and management of infrastructure.
Engineering projects rarely go as planned, so the need to establish contingency strategies is crucial. Trouble can arise upon carrying out day-to-day tasks, sometimes omitting crucial steps. These are because project engineers usually gather requirements, create documents, order materials, coordinate shipping, manage teams, configure processes, and troubleshoot issues. Hence, using an engineering project checklist helps ensure that the job can be done safely and efficiently.
Importance of Using an Engineering Checklist
While the term “audit” is typically associated with financial statements, its importance in the context of engineering can’t be overstated. Engineering projects involve input from several professionals that cover different disciplines, as well as a significant financial investment. Having plenty of moving parts makes a project more susceptible to delays, miscommunication, and other setbacks.
Using an engineering audit checklist helps your team implement a proactive and systematic approach to managing engineering projects. They can also become more vigilant by making data visibility and collaboration easier. In doing so, production mistakes can be avoided, issues are quickly identified and immediately resolved, and engineering projects are completed with little to no problem.
Whether in construction, manufacturing, software development, or any other engineering discipline, audit checklists are invaluable tools that contribute to the success of projects and processes.
What to Include in One
To help you create an effective engineering checklist, make sure to include the following key elements and sections:
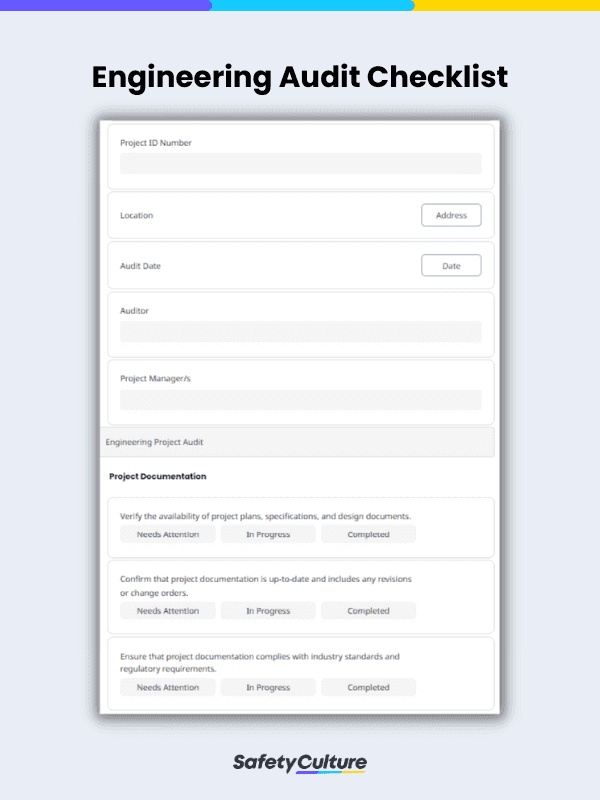
- Project Overview – Include essential project information, such as the project name, identification number, and the names of the auditor and project manager/s.
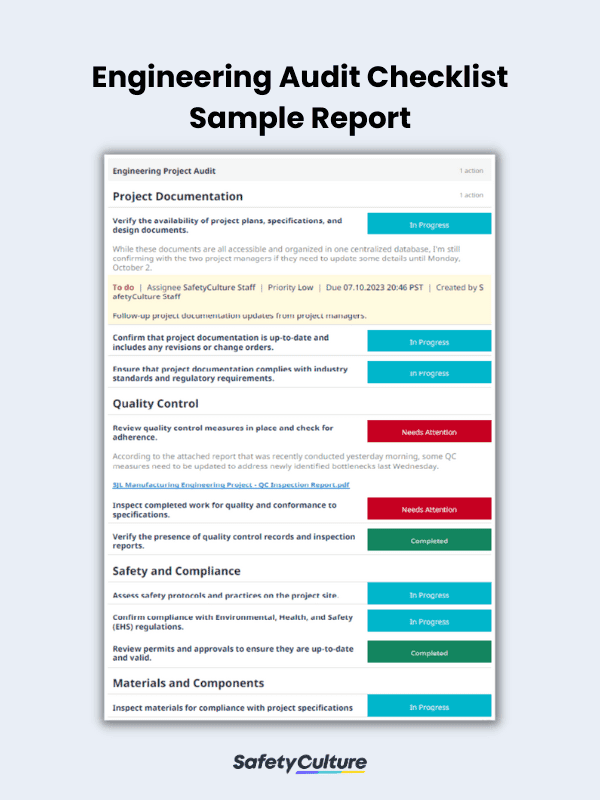
- Project Documentation – Verify the availability and timeliness of project plans, specifications, and design documents.
- Quality Control (QC) – Review QC measures in place and inspect completed work for quality and conformance to specifications.
- Safety and Compliance – Confirm adherence to safety protocols, regulatory requirements, and Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) standards.
- Materials and Components – Verify the quality of critical components and their conformity to design requirements.
- Testing and Validation – Confirm that tests and validations have been conducted and recorded.
- Documentation and Recordkeeping – Ensure that all project-related documentation is complete, up-to-date, and readily accessible.
- Regulatory Compliance – Assess compliance with relevant industry codes and standards.
- Project Schedule and Budget – Confirm that the project is on budget and that cost control measures are in place.
- Communication and Collaboration – Document any meetings or discussions related to the project.
- Completion and Handover – Review project closeout procedures and documentation.
- Lessons Learned and Continuous Improvement – Identify areas for process improvement and make recommendations.
How to Create and Use an Effective Engineering Checklist
For this sample guide, know how to create and use your own engineering checklist for audits to maximize its effectiveness:
- Create a user-friendly, organized checklist using digital tools or templates. Make sure to use clear headings and sections to make the checklist items easy to follow.
- Detail is key. Make sure to include all the necessary information.
- Use plain language and concise questions to gather information.
- Set your own questions, add signatures, and build out your inspection checklist.
- Preview the template to ensure it’s correct before exporting and deploying to teams.
- Train engineers, project teams, and others who will use it on how to properly use the checklist.
- Share your template with your team and start auditing.
- Regularly review and update the checklist to reflect changes in project requirements, industry standards, or best practices.
FAQs About Engineering Checklists
Yes, engineers can use these checklists to systematically identify and address weaknesses, deviations, and recurring issues in their processes or projects. The data collected from completed checklists provides valuable insights for optimizing procedures, introducing best practices, and enhancing overall efficiency.
Yes, engineering checklists provide a structured framework for auditors to review and verify compliance with industry regulations and standards. These checklists ensure that all relevant aspects of a process or project are thoroughly assessed, helping organizations demonstrate adherence to legal requirements.
Engineers can leverage digital checklist tools and mobile apps that offer offline functionality for them to be remotely accessible. These tools enable them to create, update, and complete engineering checklists using smartphones, tablets, or laptops, even when internet connectivity is unreliable.